Semi-Supervised Learning of MRI Synthesis without Fully-Sampled Ground Truths
Aug 16, 2022· ,,,,,·
0 min read
,,,,,·
0 min read
Mahmut Yurt
Onat Dalmaz
Salman Dar
Muzaffer Ozbey
Berk Tınaz
Kader Oguz
Tolga Cukur
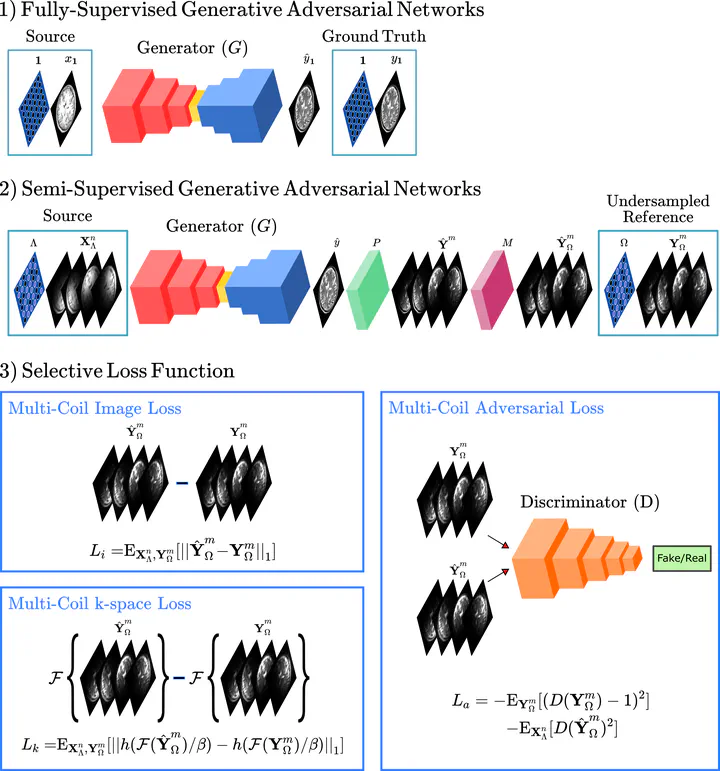 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
Learning-based translation between MRI contrasts involves supervised deep models trained using high-quality source- and target-contrast images derived from fully-sampled acquisitions, which might be difficult to collect under limitations on scan costs or time. To facilitate curation of training sets, here we introduce the first semi-supervised model for MRI contrast translation (ssGAN) that can be trained directly using undersampled k-space data. To enable semi-supervised learning on undersampled data, ssGAN introduces novel multi-coil losses in image, k-space, and adversarial domains. The multi-coil losses are selectively enforced on acquired k-space samples unlike traditional losses in single-coil synthesis models. Comprehensive experiments on retrospectively undersampled multi-contrast brain MRI datasets are provided. Our results demonstrate that ssGAN yields on par performance to a supervised model, while outperforming single-coil models trained on coil-combined magnitude images. It also outperforms cascaded reconstruction-synthesis models where a supervised synthesis model is trained following self-supervised reconstruction of undersampled data. Thus, ssGAN holds great promise to improve the feasibility of learning-based multi-contrast MRI synthesis.
Type
Publication
IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging